Notice
Recent Posts
Recent Comments
Link
| 일 | 월 | 화 | 수 | 목 | 금 | 토 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 |
| 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 |
| 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 | 20 | 21 |
| 22 | 23 | 24 | 25 | 26 | 27 | 28 |
Tags
- 밑바닥부터시작하는딥러닝
- Apache
- Selenium
- 생활코딩
- word2vec
- 예제중심HTML&자바스크립트&CSS
- 논문리뷰
- 머신러닝
- 한빛아카데미
- attention
- MySQL
- deeplearning
- 컴파일설치
- 크롤링
- 셀레니움
- CBOW
- Crawling
- AndroidStudio를활용한안드로이드프로그래밍
- image
- Lamp
- 밑바닥부터시작하는딥러닝2
- 딥러닝
- 수동설치
- 비지도학습
- 프로그램새내기를위한자바언어프로그래밍
- 가비아
- aws
- jupyter
- 한빛미디어
- 소스설치
Archives
- Today
- Total
안녕, 세상!
EPSANet : An Efficient Pyramid Squeeze Attention Block on Convolutional Neural Network 정리 본문
It공부/딥러닝논문리뷰
EPSANet : An Efficient Pyramid Squeeze Attention Block on Convolutional Neural Network 정리
dev_Lumin 2022. 2. 21. 12:30Abstract
- EPSANet
- Novel lightweight and effective attention method
- Replacing the 3x3 convolution with the PSA module in the bottleneck blocks of the ResNet
- Be developed by stacking ResNet-style EPSA blocks
- Strong multi-scale representation ability for various computer vision tasks
- Outperforming most of the state-of-the-art channel attention methods
Introduction
- Specifically two types of attention methods
- 1) Channel attention
- Ex) Squeeze-and-extraction (SE module)
- → Ignores the importance of spatial information
- 2) Spatial attention
- 1) Channel attention

Problems
- 1) How to efficiently capture and exploit the
spatial informationof the feature map withdifferent scalesto enrich the feature space - Different scales를 가진 feature map의 spatial information을 어떻게 효율적으로 잡아내고 이용할 지
- 2) Channel or spatial attention can only effectively capture the local information but fail in establishing
a long-range channel dependency
Solution
- Pyramid Squeeze Attention (PSA)
Low-costandhigh-performancenovel module- Using
multi-scale pyramid convolutionstructure - → to integrate the information of the input feature map*
- Cross-dimension interaction
- By extracting the channel-wise attention weight of the multi-scale feature maps
Contribution
- 더 세분화된 level에서 multi-scale spatial information을 효율적으로 추출할 수 있는 EPSA block을 제안함
- EPSA block은 매우 flexible하고 scalable하기에 computre vision의 많은 task에 대해서 다양한 network architectures에 적용될 수 있음
- EPSA block은 더 풍부한 multi-scale feature representation을 배울 수 있고 cross-dimension channel-wise attention weight를 유동적으로 재조정할 수 있음
2. Related work
- 이전 연구들의 더 많은 computational cost가 요구되는 정교한 attention modules를 설계에 집중하거나 long-range channel dependency를 설립할 수 없었음
- PSA를 제안하여 low model complexity를 가진 attention weight를 학습하는것을 목표로 두게하고, long-range channel dependency를 설립하기 위해 local과 global attention을 효율적으로 통합함
3. Method
3.1 Revisting Channel Attention
Channel attention
- SE block



- With two fully-connected layers, the linear information among channels
- Be helpful for the interaction of the information high and low channel dimensions
- The above one is named
SEWeight module
3.2 PSA Module

- Be implemented in four steps
- 1) Multi-scale featue map on channel-wise는
Squeeze and Concat (SPC)를 수행함으로써 얻어짐 - 2) Channel-wise attention vector은 다른 scales를 가진 feature map의 attention을 추출하는
SEWeight module을 사용함으로써 얻어짐 - 3) 재보정된 multi-scale channel의 weight는 channel-wise attention vector을 재보정하는 Softmax를 사용함으로써 얻어짐
- 4) Element-wise 곱의 계산은 weight와 일치하는 feature map을 재보정하는데 적용됨
- 1) Multi-scale featue map on channel-wise는
- 최종적으로 multi-scale feature information가 풍부한 refined feature map을 output으로 얻을 수 있음
SPC module
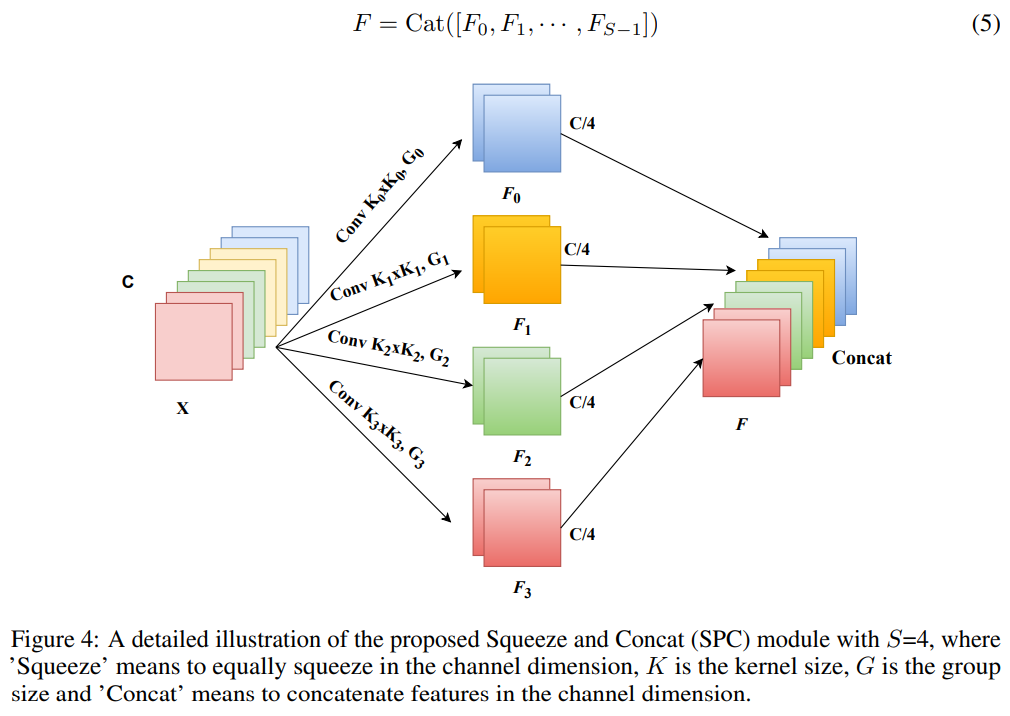
- 제안된 PSA에서 multi-scale feature extraction을 수행하기 위한 핵심 연산은
SPC임 - Input feature map의
Spatial information은 multi-branch 방식으로 추출함 - → By doing this, They can obtain more abundant positional information of the input tensor
- Using
multi-scaleconvolutional kernels in apyramid structure - → Different spatial resolutions and depths can be generated
- $C$ : The input channel dimension of each branch
- $S$ : Number of branches
- $C'=C/S$ : $F_i$’s channel dimension ( $i=0,1,...,S-1$ )
- $C$ should be divisible by $S$
- 각 branch에 대하여 multi-scale spatil inforamtion을 독립적으로 학습하고,
local 방식으로cross-channel interaction을 형성함 - Parameters의 양에 대한 큰 향상은 kernel sizes의 증가와 함께 초래할 것임
- Computationa cost를 증가시키지 않으면서 서로 다른 kernel scales의 input tensor을 처리하기 위해서
Group convolution을 사용함
Grouped Convolution
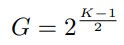

- $G=2^{(k_i-1)/2}$ : Group size
- $k_i=2\times(i+1)+1$
- $F_i\in R^{C^`\times H \times W}$
- $F\in R^{C \times H \times W}$ : Obtained multi-scale feature map

- By extracting the channel attention weight information from the multi-scale pre-processed feature map, the attention weight vectors with different scales are obtained
- $Z_i\in R^{C^` \times 1 \times 1}$ : Attention weight

- Concatenate the Attention weights
- → In order to realize the interaction of attention information and fuse the cross-dimensions vector without destroying the original channel attention vector
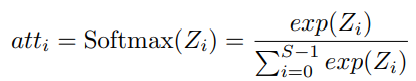
- Be used to adaptively select different spatial scales
- By doing this, the interaction between
local and global channel attentionis realized
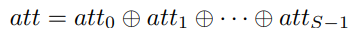
- $att_i$들도 concatenate시킴

- Attention weight과 $F_i$ channel-wise multiplication 계산

- Concatenation 계산이 summation보다 더 효율적
- Original feature map의 정보를 제거하지 않으면서 feature representation을 유지할 수 있기 때문
- PSA module can integrate the
multi-scale spatial informationandthe cross-channel attentioninto the block for each feature map
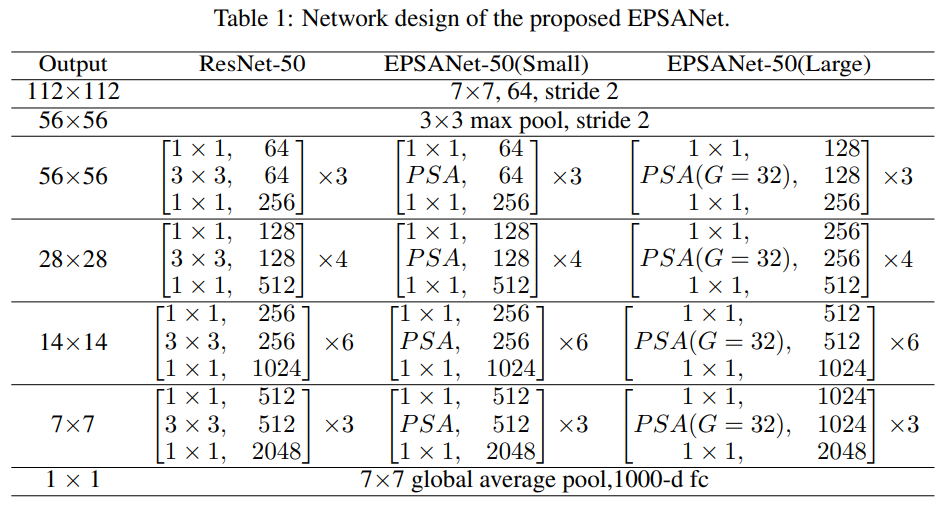
3.3 Network Design

- Be further obtained by replacing the 3x3 convolution with the PSA module at corresponding positions in the bottleneck blocks of ResNet
- Multi-scale spatial information과 cross-channel attention이 통합되어 있기에 multi-scale spatial information을 더 세분화된 수준에서 추출할 수 있고
long-range channel dependency를 구축할 수 있음 - EPSANet은 제안된 EPSA blocks를 ResNet style로 쌓음으로써 구축됨
- Structure of EPSANet
4. Experiments
4.1 Implementation Details
- Image classification tasks에 대해서는 ResNet를 backbone model로 사용하고, ImageNet dataset으로 experiments를 수행함
- The standard augmentation scheme는 실행되었고, input tensor의 크기는 랜덤하게 horizontal fliping 과 normalization에 의해서 224x224로 잘림
4.2 Image Classification on ImageNet

- 전반적으로 더 적은 parameters와 낮은 computational cost로 더 좋은 정확도를 성취하거나 state-of-the-art 기록을 냄
4.3 Object Detection on MS COCO
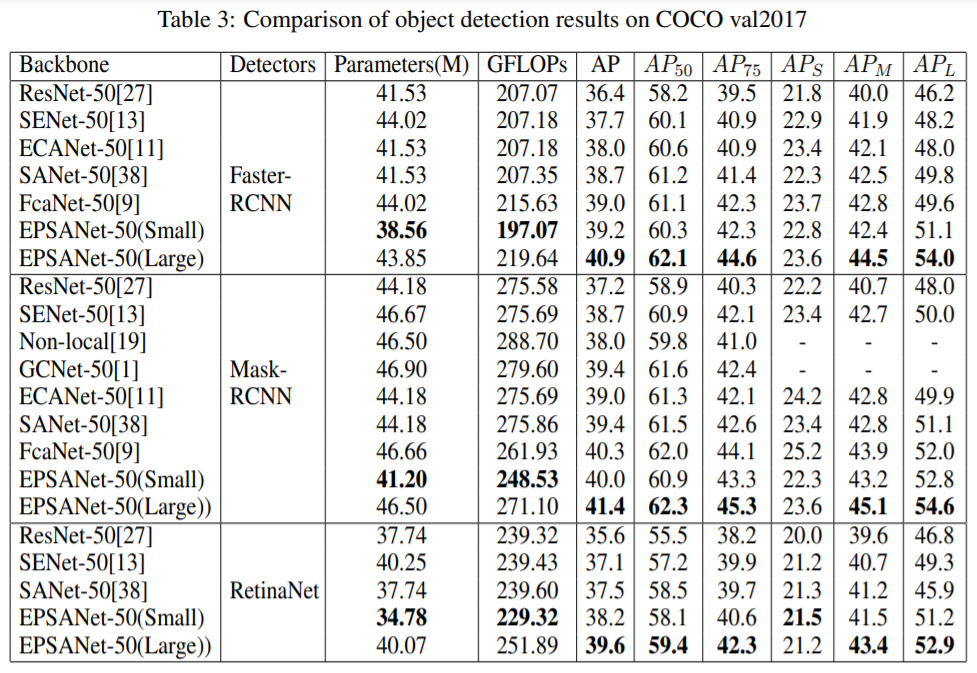
- EPSANet-50(Small) outperforms the SENet-50 by a large margin with less parameters and lower computational cost
- The EPSANet-50(LARGE) can achieve the best performance compared with the other attention methods
4.4 Instance Segmentation on MS COCO

- Propsed PSA module outperforms the other channel attention methods by a considerably larger margin
- These results verified the effectiveness of proposed PSA module
4.5 Ablation Study

- Adjusting the group size to verify the effectiveness of prorposed network on the ImageNet dataset
- Computatilnal cost를 증가시키지 않고 spatial domain에서 multi-scale의 location information을 이용하기 위해서, 서로 다른 scale을 가진 각 feature map에 대해 독립적으로 group convolution을 적용함
- 가장 밑의 결과가 비교적 균형잡힘
5. Concolusion
- 제안된 PSA module은 multi-scale spatial information과 channel attention vector안의 dimensions에 대한 중요한 features를 추출할 수 있음
- 제안된 EPSA block은 multi-scale representation능력을 더 세분화된 수준으로 향상시킬 수 있고 long-range channel dependency를 발전시킬 수 있음
- 제안된 EPSA Net은 multi-scale contextual features와 image-level categorical information을 효율적으로 통합할 수 있음
My Opinions
- Softmax를 전체 $Z$에 적용한것이 아닌 각 spatial 정보를 담고 있는 하나의 $Z_i$에 적용했기 때문에 local한 정보가 포함되어 있고 이러한 $att_i$들을 concatenate한 후 multi-scale channel인 $F_i$에 attention으로 전체적으로 적용했기 때문에 global 정보를 담고 있다고 볼 수 있다고 생각하는것 같음
- 그런데 softmax를 전체에 취하지 않는 저런 형식은 local정보는 잡는다는것은 납득이 가지만 서로 다른 multi-scale들 중에서 비교적 어떤것을 더 집중해서 볼 지에 대한 관계는 좀 약할것 같음
- 내 생각은 이미지를 볼 때 큰 filter 특징, 작은 filter 특징 모두 고려하고자 하는 차원에서 하면 저렇게 local하게 softmax하는것은 맞다고 동의함
github link
(논문에 존재)
참조 :
'It공부 > 딥러닝논문리뷰' 카테고리의 다른 글
Comments




